How to Setup Ingress on Minikube Kubernetes with example
If you are learning Kubernetes then you might had heard of Ingress object which is used to allow external network access to the Kubernetes cluster. For doing a hands on, Minikube is one of the widely used software which setups Kubernetes environment. In this article, I am going to show you how to enable Ingress in Minikube and a example on how to use it.
Before You Begin
If you are new to Minikube and haven't installed it yet, then refer to the below article for the installation steps.
- Install Kubernetes using Minikube on Linux, CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat
You should have a working Minikube setup and dashboard. The kubectl tool must be installed and working in tandem with Minikube.
Start Minikube
minkube start
Enable Ingress Controller
- Run the following command to enable the NGINX Ingress controller:
minikube addons enable ingress
- Verify whether Ingress controller is running or not:
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
Use Kubernetes Dashboard as application
Since Ingress controller is enabled and ready for use, lets deploy Ingress service for Minikube Kubernetes dashboard.
- Get the Kubernetes dashboard details which is present in kubernetes-dashboard namespace by running following command:
kubectl get all -n kubernetes-dashboard
Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/dashboard-metrics-scraper-7976b667d4-f6q74 1/1 Running 6 23d pod/kubernetes-dashboard-6fcdf4f6d-ghq97 1/1 Running 12 23d NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.100.4.35 <none> 8000/TCP 23d service/kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.110.150.181 <none> 80/TCP 23d NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper 1/1 1 1 23d deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard 1/1 1 1 23d NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper-7976b667d4 1 1 1 23d replicaset.apps/kubernetes-dashboard-6fcdf4f6d 1 1 1 23d
- Note down the Kubernetes dashboard service name and port (highlighted in above output) which will be used to create ingress resource.
Create Ingress Resource and Validate
- Let's create a ingress resource using dashboard-ingress.yaml file with below contents:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: dashboard-ingress
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
rules:
- host: kub-dashboard.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: kubernetes-dashboard
port:
number: 80
- In the above file, apiVersion and kind denotes ingress resource.
- The name of the resource will be dashboard-ingress which will be created under kubernetes-dashboard namespace. Note that we are not using default namespace here because kubernetes-dashboard is present in kubernetes-dashboard namespace.
- Under specification we define host name as kub-dashboard.com as an example here. You can use any domain here as we will be creating host file entry later. Under http, provide path to which dashboard opens, service name to use and port number on which service is exposed. If you recollect, this information is already gathered in previous step.
- Let's create ingress resource using the above file now by running following command:
kubectl apply -f dashboard-ingress.yaml
Output:
ingress.networking.k8s.io/dashboard-ingress created
- Get the ingress resource details like IP and port by running following command:
kubectl get ingress -n kubernetes-dashboard
Output:
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE dashboard-ingress <none> kub-dashboard.com 192.168.99.100 80 3m53s
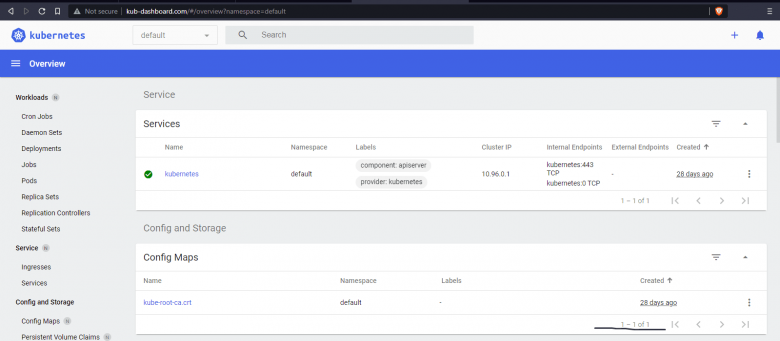
- We have specified domain name kub-dashboard.com in ingress resource file. Let's create a local host file entry on system and point it to the IP 192.168.99.100 which is assigned by ingress service as in above output.
- After adding the entry, browse the domain kub-dashboard.com and you should see the kubernetes dashboard displayed as in following image:
Do you have any additional comments, questions, or concerns you would like to share? Please post in comments section.